Unification of the Forms of Localized Corrosion | Digby Macdonald
Summary :
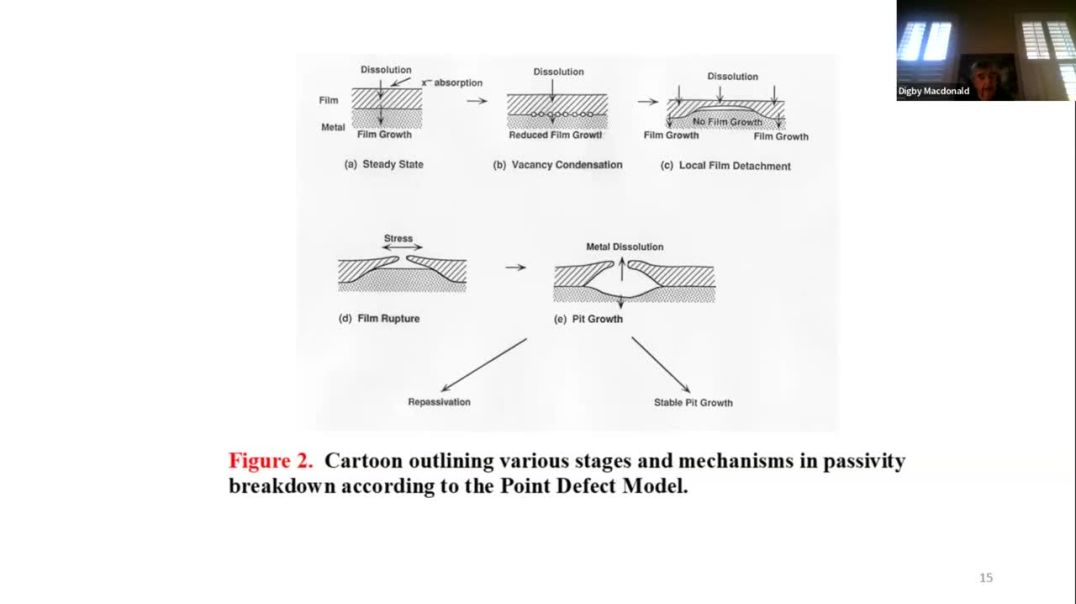
The various forms of localized corrosion, including pitting corrosion (PC), stress corrosion cracking (SCC), corrosion fatigue (CF), electropolishing (EP), and flowassisted corrosion (FAC) are generally treated as separate phenomena although the fall under the umbrella of the differential aeration hypothesis (DAH). In this paper, I reveal a theoretical basis, in addition to the DAH, for unifying all forms of localized corrosion. The treatment makes use of the condition imposed by the Point Defect Model (PDM) for defining the conditions for the passivity of a metal and inquiring as to the events that occur at the point of nucleation. For example, in the case of passivity breakdown, which is the precursor to pitting, it is essential for the barrier oxide layer to be prevented from continued growth into the substrate metal. This occurs via condensation of cation vacancies on the cation sublattice at the metal/barrier layer interface such that the barrier layer is no longer in contact with the metal. However, outside of the nucleus, the barrier layer is still in contact with the metal and growth of the barrier layer into the metal continues via the generation of new (film) cations and oxygen vacancies. Simultaneously, dissolution of the battier layer continues at the barrier layer/solution interface with the result that the barrier layer thins preferentially over the pit nucleus. At some point the barrier layer “cap” over the nucleus ruptures allowing the intrusion of water and eventually to the establishment of differential aeration. At that point, the cavity actively grows to form an active pit.
About Author :
Digby D. Macdonald is Professor in Residence in the Departments of Nuclear Engineering and Materials Science and Engineering at the University of California at Berkeley. He specializes in the growth and point defect structures of thin oxide films on metal surfaces and developed the Point Defect Model for describing such systems. He also developed the modern theory of stress corrosion cracking, corrosion fatigue, and pitting corrosion in terms of the deterministic Coupled Environment Models and is a pioneer modern Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. One of his major activities is the modeling of the electrochemical and corrosion properties of structural materials in the coolant circuits of operating, water-cooled nuclear reactors. He has published more than 1000 papers in peer-reviewed journals and conference proceedings and four books. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, the Royal Society of New Zealand (the “National Academies” of those countries.