Latest videos
Summary :
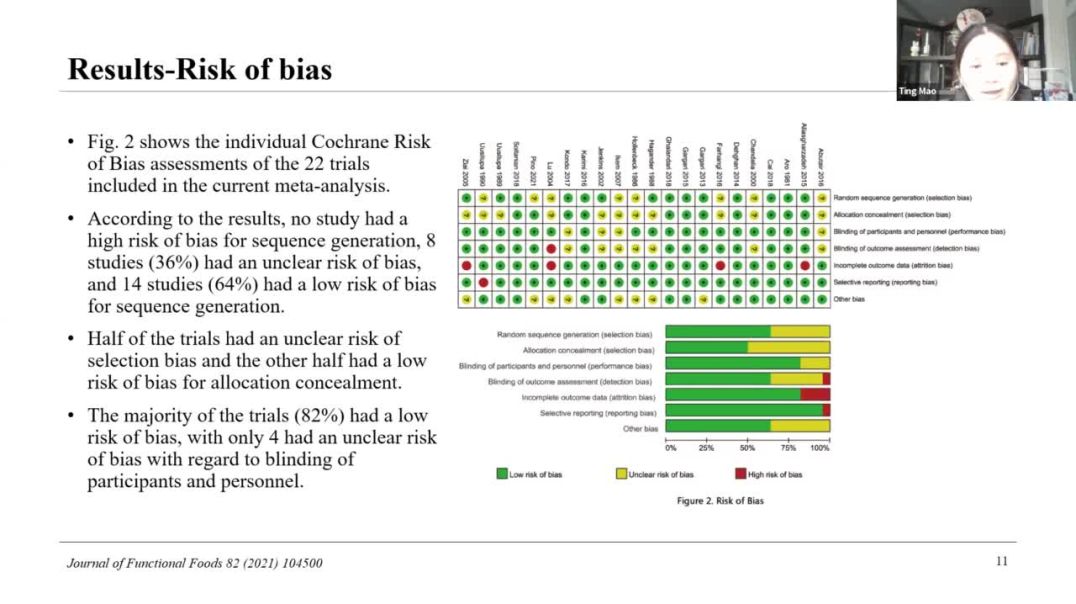
This review aimed to assess the effect of dietary fiber on short-term and long-term glycemic control and insulin responses in T2DM patients. Five electronic databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in English and investigating one primary outcome—glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and six secondary outcomes—fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin, Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), two-hour postprandial glucose, two-hour postprandial insulin, and body mass index (BMI) through March 23, 2021. Of 3266 identified studies, 22 eligible RCTs comprising 911 participants with T2MD were included. Among them, 16 studies used soluble fiber and the rest used fiber from natural foods. Subgroup analysis demonstrated that soluble fiber was more efficient in controlling HbA1c and FBG than fiber from natural foods. Compared with the control, dietary fiber at a median dose of 10 g/day for a median intervention duration of 8 weeks significantly reduced HbA1c, FBG, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR. In conclusion, both soluble fiber products and fiber from natural foods are effective in improving glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in T2MD patients, the former yielding better effects. However, due to most of the evidence from rather short-term trials and the detected significant between-study heterogeneity, further long-term and high-quality RCTs are needed.
About Author :
I am a register dietitian and psychological consultant in China. I got my master’s degree in Nutrition and Dietetics in Saint Louis University and after that, I came back to China to work as a dietitian for around 7 years and now I am pursuing my PhD in Food Science in Lincoln University. My research is mainly focus on exploring the health effects of bioactive ingredients such as dietary fiber and polyphenols. I am also interested in discovering milk proteins as delivery vehicles for beneficial compounds.
Summary :
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) report, 35,000 diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) in 2017 (1). Improving glycemic control decreases the risk of diabetic complications. Annual cost of treating diabetic patients with complications was US$11,706.9 compared with US$2746.7 for treating those without complications (2). Using FGM gives more insight for the physician and patient to manage diabetes, and thus, improve glycemic control.
About Author :
Bachelor’s degree in pharmaceutical science, king Saud university 2012 Master’s in health informatics, king Saud university 2020 Senior pharmacist at Prince Sultan Cardiac center.
Summary :
As of today, approximately over 400 million adults are diagnosed with Diabetes, and another 300 million adults have been found to have shown impaired glucose tolerance, and render at a high risk for developing the disease. The clinical condition wherein men show the symptoms and biochemical evidences of deficient testosterone levels is known as male hypogonadism, and it, with stern evidences, has been to be prevalent, with a greater tendency, in men with type 2 diabetes. Low testosterone is associated with diminished libido, erectile dysfunction, increased fat mass, decrease muscle, bone mass and energy, depression and anaemia.Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism related with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus has been an ever growing concern, and we shall be discussing the implications and co-effects of this, in this session.
About Author :
Shikhar Tripathi is a medical student, researcher and an author. Even as a student, he has published multiple research as well as review articles, which have received global acclaim, and has authored two medical reference books. One of his articles, where he gave a hypothesis on vertical transmission of COVID-19 from pregnant mother to fetus, was well acclaimed world wide and even got featured by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in their repository and also got featured amongst the references on COVID-19 researches, on Wikipedia. He has been a guest speaker for the Young Researcher’s Forum at International Conference on Diabetes, Hypertension and Metabolic Syndrome 2020, International Conference on COPD and Asthma 2021 and is slated to be a guest speaker at International Conference on Clinical & Pharmaceutical Microbiology, 2021 (to be held in November 2021).
Summary :
This cross-sectional, web-based study included Saudi adult patients with T1DM who attended at least one virtual phone visit with the diabetes clinic at King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, between August 1 and December 31, 2020. Patients anonymously answered a Google form- created Arabic questionnaire. Information about patient characteristics, outcome, and perception of the virtual phone visit were obtained. Data were presented using descriptive statistics, chi-square, one- way ANOVA, independent t-, and Welch’s t-tests.
Summary :
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an endocrine disease characterized by hyperglycemia. According to WHO, 422 million people worldwide have diabetes and it is one of the leading causes of death in the world. α-Glucosidase and α-amylase can hydrolyze carbohydrates; thus, inhibitors of these enzymes are considered useful drug candidates for type II DM therapy. Long-term use of synthetic enzyme inhibitors, such as acarbose, may cause various side effects, such as flatulence and abdominal problems. Natural α-glucosidase inhibitors have thus been presented as a better alternative to control postprandial hyperglycemia as they exhibit minor or no side effects. The aim of this study is the scientific investigation of antihyperglycemic effect of 70% methanol extracts prepared from 32 plants used traditionally against diabetes in Turkey. The plants were collected from Erzurum and its environs in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Then, they were dried, powdered, and extracted. The extracts were evaluated for in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. The inhibitory activity was determined spectrophotometrically by measuring the quantity of p-nitrophenol released from p-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside at 405 nm. Cotinus coggygria (leaves), Rhus coriaria (fruits), Viburnum opulus (fruits), Viburnum lanata (fruits), Paeonia mascula (aerial parts), Elaeagnus angustifolia (leaves), Elaeagnus rhamnoides (leaves), Paliurus spina-christi (fruits), Pinus sylvestris (cones), Juniperus foetidissima (cones), Juniperus oxycedrus (cones), and Prunus spinosa (fruits) showed the potent inhibitory activity with >90% inhibition at 5 mg/mL when compared with acarbose as a standard drug with 67% inhibition at same concentration. In addition, the compounds responsible for α-glucosidase inhibitory activity were isolated from some of these plants.
About Author :
She graduated from Atatürk University, Faculty of Pharmacy in 2013. She graduated and get PhD from Atatürk University Health Sciences Institute in 2020. She has been working as a Research Assistant at Atatürk University, Faculty of Pharmacy since 2014. While continuing her doctoral education; within the scope of Erasmus+ Program, she conducted studies in her field under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Karel Smejkal (VFU, Brno/Czechia) in 2017; Prof. Dr. Rudolf Bauer (Graz University, Graz/Austria) in 2020. She also works as a researcher and educator at Atatürk University Medicinal and Aromatic Plant and Drug Research Center. Her research areas are as follows: Phytochemistry, Biological activities (in vitro alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase activities, antioxidant activities), Analytical pharmacognosy.
Summary :
Diabetes is a multifactorial disease with complex multi-organ-multi-target crosstalk in the body. While the currently available molecular drugs effectively reduce hyperglycemia, they are inadequate to address the multifactorial etiopathology, chronicity and systemic complications of diabetes. A more holistic and systemic approach is essential for the successful management diabetes and associated metabolic diseases. We hypothesize an integrative diabetes management strategy, combining holistic principles of diabetes management with its molecular understandings, would be more appropriate to fill this gap. We propose a novel trans-disciplinary ‘Ayurveda-Biology’ approach for deepening the holistic understanding of the pathophysiology of diabetes as well as designing novel integrative strategies for managing diabetes and restoring whole body glucose homeostasis. While Ayurveda and modern biomedicine uses different epistemology and ontology for describing diabetes, both the systems recognize the central role of gut and gut derived factors in postprandial glucose disposal and whole body glucose homeostasis. Essentially, the principles of both Ayurveda and modern biomedicine overlap at a gut centered view of diabetes management; and Gastro-intestinal mediated glucose disposal, a holistic concept of glucose metabolism. Therefore, an integrative disease management strategy, focusing on an Ayurveda Biology framework, would be the prerogative for successful management of diabetes. This can also offer novel strategies for cost effective, holistic and multi-targeted management of diabetes.
About Author :
A researcher, trained in cell biology and molecular biology, with more than 10 years of research and teaching experience at various institutes and Universities in India and South Korea. Interested in medical pluralism and integrative medicine for wellness and disease management. My research interests are metabolic diseases, with special focus on glucose metabolism and its role in obesity and diabetes. Our team is working on creating trans-disciplinary knowledge framework between Ayurveda, the traditional Indian System of Medicine (ISM) and modern biology for delineating the complex biology of metabolic homeostasis and metabolic diseases. Our team envisage that the effective merger of both holistic and reductionist views of biology is imperative for successful health and disease management. Recognizing and logically bridging epistemologically and culturally different perspectives of health and disease management would have significant contribution in the contemporary healthcare sector, particularly in the management of chronic lifestyle diseases.
Summary :
M. pumilum has been claimed to protect the bone against the adverse effect of estrogen deficiency. Additionally, it also exhibits anti-diabetic activity. In view of these, this study aims to identify the mechanisms underlying the bone protective effect of M. pumilum in the presence of both estrogen deficiency and diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods: Ovariectomized, diabetic female rats were given M. pumilum leave aqueous extract (MPLA) (50 and 100 mg/kg/day), estrogen, glibenclamide and estrogen plus glibenclamide for 28 consecutive days. At the end of the treatment, fasting blood glucose (FBG), serum insulin, Ca2+, PO4 3- and bone alkaline phosphatase (BALP) levels were measured. Rats were sacrificed and femur bones were harvested for determination of expression level and distribution of RANK, RANKL, OPG and oxidative stress and inflammatory proteins by molecular biological techniques.
About Author :
Dr. Giribabu Nelli, Senior Lecturer in the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya. In 2011 November, Dr. Giribabu Nelli completed his Ph.D. in reproductive and developmental biology at the Department of Zoology, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, India. From 2013 to 2016, he worked as a postdoctoral fellow at the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, the University of Malaya. In the same Department, he was recruited as a Senior Lecturer in November 2016. He has now published 61 ISI publications with a high impact factor, as well as two book chapters and two patents (Filed) with achieved 6 grants. His main research interests on diabetes and their complications, obesity, natural products and male and female reproductive physiology.
Summary :
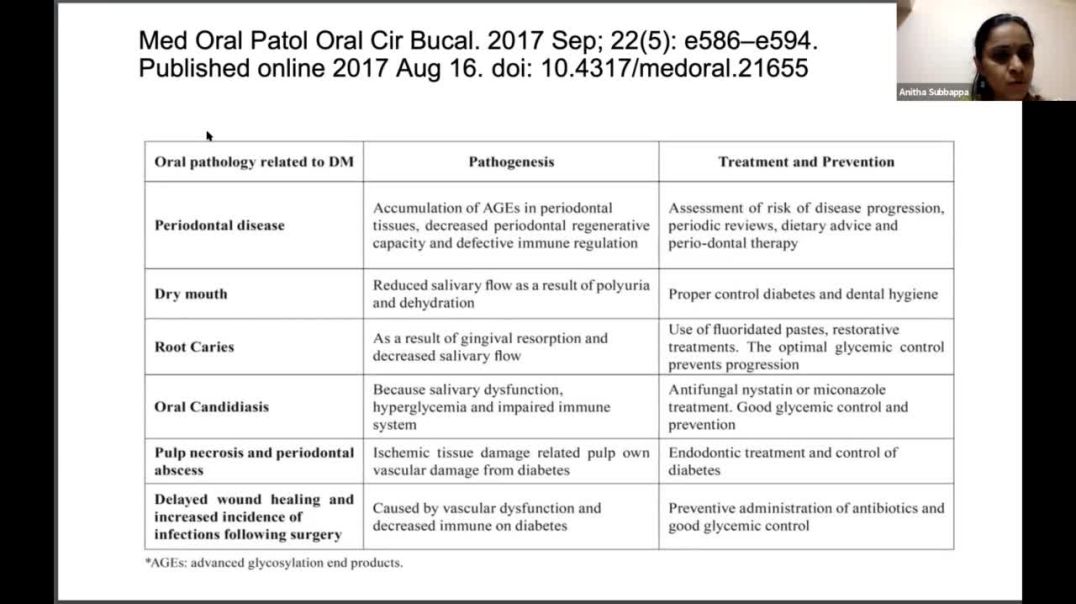
Diabetes mellitus, a major lifestyle disease, has become a global burden. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF), Diabetes Atlas (2015), reports that there are 415 million people diagnosed with diabetes representing 8.8% of adults aged 20–79 years. A knowledge on oral lesions to help diagnose a case of diabetes which would also require a referral to endocrinologist. Also a 2 way link has been established between diabetes & periodontitis. A physician/endocrionologist/diabetologist needs to be aware of oral changes to be able to form an interdisplinary unit for a comprehensive handling of patients. An awareness of periodontitis as the 6th Complication of Diabetes is also important. Dental caries/periodontitis, black hairy tongue, candidiasis, Xerostomia & other mucosal lesions are also a frequent finding in diabetic patients. A knowledge on the oral changes and its entity in diabetic complications stresses the importance of dental element in diabetes.
About Author :
She is a Reader in the Department of periodontology, JSSDCH, JSSAHER with 20 years experience. She has authored national and international publications. She has presented papers nationally and internationally, won nationally and international awards. She is a Laser Specialist from SOLA, University of Vienna. She is an implantolgist. She has been a Speaker in National Conferences. She is the Team Leader of Special Interest Group “Diabetes & Oral Care.” She is a member of Geriatric clinic at JSS Multi Speciality Hospital. She is a reviewer in various journals. She has been a chairperson, judge/panelist at conferences. She has organized various webinars/conferences/epaper/eposter competitions. he is a member at various Dental societies. She has authored a book. She has guided Undergraduates/postgraduate research/paper presentations, winning awards.
Summary :
A series of alloy system take place in a class of functional materials due to stimulus response to external effect. Shape memory alloys take place in this group by exhibiting a peculiar property called shape memory effect. This phenomenon is characterized by the recoverability of two certain shapes of material at different conditions. Shape memory effect is initiated with thermomechanical processes on cooling and deformation, and performed thermally on heating and cooling, with which shape of the materials cycle between original and deformed shapes in reversible way. Therefore, this behavior can be called Thermal Memory or Thermoelasticity. This deformation is plastic deformation, due to the soft character of the material in low temperature condition, deformation energy is stored in the material and released on heating by recovering the original shape. These alloys are used as shape memory devices in many fields such as medicine, metallurgy, building industry. This property is result of two displacive transformations, thermal and stress induced martensitic transformations. Thermal induced martensitic transformation occurs on cooling with cooperative movements of atoms by means of lattice invariant shears in <110 > -type directions on the {110} - type planes of austenite matrix, along with lattice twinning and ordered parent phase structures turn into the twinned martensite structures. Twinned structures turn into the detwinned structures by means of stress induced martensitic transformation, by stressing material in the martensitic condition. Atomic movements are confined to the neighbor atom distances, and martensitic transformations are diffusionless or displacive transformations.
About Author :
Dr. Adiguzel graduated from Department of Physics, Ankara University, Turkey in 1974 and received PhD- degree from Dicle University, Diyarbakir-Turkey. He has studied at Surrey University, Guildford, UK, as a post- doctoral research scientist in 1986-1987, and studied were focused on shape memory effect in shape memory alloys. His academic life started following graduation by attending an assistant to Dicle University in January 1975. He became professor in 1996 at Firat University in Turkey, and retired on November 28, 2019, due to the age limit of 67, following academic life of 45 years. He supervised 5 PhD- theses and 3 M. Sc- theses and published over 80 papers in international and national journals; He joined over 120 conferences and symposia in international level with contribution. He served the program chair or conference chair/co-chair in some of these activities. Also, he joined in last six years (2014 - 2019) over 60 conferences as Keynote Speaker and Conference Co-Chair organized by different companies. Additionally, he joined over 120 online conferences in the same way in pandemic period of 2020-2022. Dr. Adiguzel served his directorate of Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Firat University, in 1999- 2004. He received a certificate awarded to him and his experimental group in recognition of significant contribution of 2 patterns to the Powder Diffraction File – Release 2000. The ICDD (International Centre for Diffraction Data) also appreciates cooperation of his group and interest in Powder Diffraction File.
Summary :
A solid-solid reaction took place at 1000°C during 4 h, using a mixture of pure iron oxide- Fe2O3 and pure zinc oxide – ZnO in order to synthesize zinc ferrite-ZF of different compositions: (S1) Fe2O3/ZnO:3/2, (S2) Fe2O3/ ZnO:1/1, (S3) Fe2O3/ZnO:4/1 and (S4) Fe2O3/ ZnO:2/1. Each of these mixtures were milling during 24 h before the thermic treatment carried out. S1, S2, S3 and S4 samples were became to M1, M2, M3 and M4 samples respectively, which after that were thermally characterized using DSC, DTA and TG techniques. In sequence the ZF produced were examined using XRD, optical and magnetic techniques, SEM & TEM. XRD analysis shows up as contains of equimolar ZF: M3 (73.20%), M4 (28.00%) and M2 (2.10%) as non-stoichiometric phases of ZF: 31.80% of Zn0.95Fe1.78O3.71 and 30.40 % of Zn1.08Fe1.92O4 in M4; Zn0.97Fe2.02O4 in M3 and 35.30% of Zn0.54Fe2.46O4 in M1. Previous studies of magnetic characterization observed a little hysteresis of this equimolar ZF. The results of estimation of the band gap energy (Eg) via the manipulation of the Kubelka-Munk theory allowed to determine that the samples M1, M2, M3 and M4 are considered semiconductors (3.66 and 3.76 eV).
About Author :
Doctor and Master Science in Materials Engineering and Metallurgy by Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro- Brazil. Now is a Senior Researcher Professor at Materials Science and Metallurgical Engineering Department of College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering - FIGMM of the National University of Engineering-UNI and Chief of Ironmaking and Steelmaking Researcher Group FIGMM UNI. Prof. Gomez-Marroquin is the founding partner and the first president of the board of directors of Metallurgy, Materials and Minerals Peruvian Association-APMMM. Today, she is working in characterizations of different nature biomass such as biochar from olive stone and chicken eggshell for recovering heavy metals from mining wastes. Has been working on the following subjects: recovering metals of Linz Donawitz sludge (LDS), Electric Arc Furnace Dusts (EAFD), and Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) using techniques of selfreduction and carbothermic reduction. Also, she had worked in reduction by CO-CO2 mixtures gases of zinc ferrite pure and zinc ferrite present into Electric Arc Furnace Dusts - EAFD using different techniques as such: X-Ray Diffraction (using the Rietveld method), Transmission Electron Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy. About ZF pure and present into EAFD, she has researches that had been onsets with the characterization of the compounds present in EAFD - Iron (III) oxide, zinc oxide & zinc ferrite - using techniques, methodologies, and equipment for thermal characterization (DTA-TGA), structural (XRD), microscopic (SEM-TEM coupled to EDS), physical (briquette porosity, specific gravity, average size & particle specific surface) and chemical analysis by Absorption Atomic and Fluorescence Spectrometer.
Summary :
Since it was first isolated graphene has proven to be one of the thinnest, strongest, most impermeable and a highly thermally and electrically conductive material. In order to enhance these properties in materials such as epoxy resins, graphene has been mixed in them. However, the graphene dispersibility and quality is not always optimal and in order to perceive an effect of graphene on the properties a high concentration must be added. Carbon Waters was founded on a groundbreaking innovative graphene production process. This process leads to already dispersed graphene, Graph’Up, that can be transferred into several matrices (Fig. 1), such as polymers and epoxy resins, which gives ready to use graphene pre-mixes for many applications (coating, composites, adhesives …). Thanks to this process highly dispersed epoxy resins are obtained and ready to be formulated. By controlling the graphene concentration mixed in epoxy resin, it is possible to increase multiple properties at low concentrations: thermal resistance, mechanical properties, hydrophobicity, thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity...The increase of several of these properties can be controlled by the graphene concentration. Adding epoxy doped graphene is now a real solution to improve the resins properties or lightening the weight of the product by either applying less of it for comparable properties or using less metal additives.
About Author :
After a PhD in polymer chemistry, Lucie Chupin worked in several academic facilities always focusing her research on bio-based and environmentally friendly polymers and materials. After working at Solvay Composites, she gained expertise in epoxy resin formulation. She then joined Carbon Waters to lead the developments of graphene-based additives for polymers and composites. Her work at Carbon Waters consists in developing high added-value products tailored to customers’ needs by integrating graphene dispersions into industrial products.
Summary :
Flexible, biocompatible electrodes are essential for the development of future wearable and implantable medical devices. While silver nanowire (AgNW) networks are promising candidates for transparent conductive electrodes (TCEs), they suffer from issues such as high roughness, low adhesion, and atmospheric corrosion sensitivity. Many flexible electrodes are made of a wrinkled conductive layer on top of a compliant substrates. Wrinkles provide a way to maintain the integrity and conductivity of the electrode while it is being stretched or bent. In this study, we report on the characterization of semi-transparent electrodes on cellulose nanopaper (CNP) substrates using a plasmaenhanced pulsed laser deposition (PE-PLD) technique. We combined AgNW with titanium nitride (TiN) layers to form wrinkled conducting nano-composite coatings with excellent electromechanical properties. Our results show that the incorporation of AgNW into TiN coatings improves the electrode’s electro-mechanical robustness. Additionally, our data show that CNP/TiNAgNW electrodes exhibit improved stability in air compared to bare AgNW coatings with improved adhesion. These findings have important implications for the development of bio-compatible flexible electronics and could pave the way for the creation of new wearable and implantable medical devices.
About Author :
Dr. Loïk Gence is a professor of the Physics Institute of the PUC university in Chile. He received the B.S., M.S. degree in electrical engineering Engineer from the Catholic University of Louvain and holds a Ph.D. in Applied Sciences from the Ecole Polytechnique de Louvain (2010) under the supervision of Dr. V. Bayot, working on the charge transport properties characterization of low dimensional organic nanostructures. With a background in experimental physics, Dr. L. Gence is specialized in nanomaterials synthesis and characterization with a strong hands-on experience in semiconductor technology and cleanroom environment. His Research experience and interests cover several fields of applied physics from Flexible and Organic electronics, Solar Energy to 2D semiconductor devices.
Summary :
A sterile dressing was devised using a combination of sodium alginate and gelatin as the most suitable polymers along with a small quantity of gellan gum (0.1%), selected out of a range of polymers to co-incorporate a pre-optimised and autoclavable curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (CSLNs) and live probiotic (Lactobacillus plantarum). The dressing was optimized for polymer concentration and other characteristics using a central composite design. It exhibited a swelling ratio of 412 ± 36%, in vitro degradation time of 3 h, optimal water vapor transmission rate of 1516.81 ± 155.25 g/m2/day, high tensile strength, low-blood clotting index, case II transport, and controlled release of curcumin. XRD indicated strong interaction between employed polymers. FESEM revealed a porous sponge like meshwork embedded with L. plantarum and CSLNs. Polyphenolics like curcumin can improve probiotic effects. Both probiotics (bacteriotherapy) and curcumin promote wound healing via antimicrobial activity, inhibition of pathogenic toxins, immunomodulation, and anti-inflammatory actions. Combination of CSLNs with probiotic enhanced (560%) its antimicrobial effects against planktonic cells and biofilms of skin pathogen, Staphylococcus aureus 9144. The dressing degraded and released L. plantarum, which germinated in the wound bed and exhibited faster wound closure and lowered bioburden in the wound area in mice. This was coupled with a decrease in wound biomarkers and antioxidant enzymes, establishing multiple healing pathways. It was as effective as the silver nanoparticle-based marketed hydrogel dressing; however, the cost and risk of developing resistance would be much lower currently.
About Author :
Dr Indu Pal Kaur is Professor of Pharmaceutics & DPIIT-IPR Chair Professor, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India. Her research forte is enhancing bioperformance of small and large molecules using active-tailored nanoparticles and electrospun scaffolds. Her group is credited with novel nanotechnologies, including 31 filed, out of which 15 Indian and 1 US patent is granted. She is US-Fulbright fellow & has received international beamtime funding at RAL, UK - 2017; 2023. She has received numerous awards including best scientist award twice, IP award, WIPO award for inventors from national and international agencies. She has produced 26 PhDs; ~70 postgraduates; received funding of almost 100 million INR from Government and Industry; delivered >75 Invited Talks; published 155 articles with H index 52.
Summary :
COVID-19 highlighted numerous failures in our global healthcare system including overcrowded hospitals, lack of preventative versus reactionary medicine, and overall missing healthcare monitoring at home. Implantable sensors include an active area of research in which materials monitor health on-demand 24 hrs a day, 7 days a week. This invited talk will discuss how implantable sensors will revolutionize healthcare enabling us to get away from the traditional oldfashion hospital based system, which clearly was not sufficient during COVID. Several examples of implantable sensors will be provided in this talk including but not limited to the growth of sensors off of medical devices that can determine bone growth, infection, and inflammation next to orthopedic implants; the use of piezoelectric implantable sensors that can sense changes in motion to detect diseases; the use of contact lenses that can sense changes in metabolites in tears to diagnose diseases; and the use magnetic materials to sense changes in magnetic fields to diagnose diseases. In all cases, such implantable sensors are not only being used to prevent and diagnose diseases but also treat diseases. Novel materials, most notably nanomaterials, have enabled the fabrication and use of such sensors across all of medicine.
About Author :
Thomas J. Webster’s (H index: 117; Google Scholar) degrees are in chemical engineering from the University of Pittsburgh (B.S., 1995; USA) and in biomedical engineering from RPI (Ph.D., 2000; USA). He has served as a professor at Purdue (2000-2005), Brown (2005-2012), and Northeastern (2012-2021; serving as Chemical Engineering Department Chair from 2012 - 2019) Universities and has formed over a dozen companies who have numerous FDA approved medical products currently improving human health. He is currently helping those companies and serves as a professor at Hebei University of Technology, Saveetha University, UFPI, and others. Dr. Webster has numerous awards including: 2020, World Top 2% Scientist by Citations (PLOS); 2020, SCOPUS Highly Cited Research (Top 1% Materials Science and Mixed Fields); 2021, Clarivate Top 0.1% Most Influential Researchers (Pharmacology and Toxicology); 2022, Best Materials Science Scientist by Citations (Research.com); and is a fellow of over 8 societies. Prof. Webster is a former President of the U.S. Society For Biomaterials and has over 1,350 publications to his credit with over 53,000 citations. He was recently nominated for the Nobel Prize in Chemistry (2023).
Summary :
Twenty two RNA therapies reached the medical market by Q1 2023. Targeted intracellular delivery remains the key requirement. For refinements of nanocarriers we focus on a bioinspired, sequence-defined process including (i) artificial amino acids (ii) precise assembly into sequences by solid phase-assisted synthesis (iii) screening for delivery and selection of top candidates. A recent chemical evolution library combined aminoethylene amino acids as polar protonatable units with novel lipo amino fatty acids (LAFs) as hydrophobic protonatable motifs. These novel double pH-responsive nucleic acid carriers utilize intracellular delivery mechanisms of both cationizable lipids and cationic polymers. The endosomal pH-dependent tunable polarity of LAF was successfully implemented by a central tertiary amine, which disrupts the hydrophobic character once protonated, resulting in drastic pH-dependent change in the logarithmic (octanol/ water) distribution logD from around +1 (pH 7.4) to -1 (pH 5.5). This “molecular chameleon character” turned out to be advantageous for mRNA, siRNA or CRISPER/Cas9 sgRNA delivery. The efficiency of best performers was up to several 100-fold higher compared to previous carriers. Transfection activity of mRNA lipoplexes was maintained even in the presence of 90% serum and at extremely low dosage of 3 pg mRNA (~2 nanoparticles/cell), in the range of the viral potency. mRNA lipoplexes showed great in vivo performance in mice with high expression levels in spleen, tumor, lung, and liver upon intravenous administration of 1 μg luciferase mRNA.
About Author :
Ernst Wagner is professor of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Center of NanoScience at LMU Munich since 2001. From 1992-2001 he was Director Cancer Vaccines, Boehringer Ingelheim (first polymer-based gene therapy trial in 1994), 1987-1995 group leader at IMP Vienna and Vienna University Biocenter, 1985-1987 postdoc at ETH Zurich, in 1985 PhD in chemistry (TU Vienna). He is Academician of European Academy of Sciences, member of CRS College of Fellows, Board member of German Society for Gene Therapy. He has authored 500 publications, with 50 503 citations, h-index 112 (GS).
Summary :
Rapid manufacturing on space/air/sea/land missions, where either gravitational force is missing or severe random disturbance may present continuously, is highly in demand. However, till today, there is no reliable technique for such working environments. The purpose of this study is to develop a technology for rapid 3D printing in solid state of polymeric materials to get rid of the problems in harsh working environment. The basic concept is to cross-link by either UV-light or photo-induced-heat of polymeric materials in the solid state for rapid volumetric additive manufacturing. The uncross-linked parts can be removed by heating or cooling for melting, or washing away by solvent. Finally, the shape memory effect (SME) of the cross-linked polymers is applied to ensure high accuracy of the printed items. We have successfully demonstrated this concept using thermal gel, UV cross-linkable vitrimer and other conventional materials.
About Author :
Dr Wei Min Huang has over 25 years of experience on various shape memory materials (alloy, polymer, composite and hybrid), he has published over 200 papers in journals, such as Accounts of Chemical Research, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, and Materials Today, and has been invited to review manuscripts from over 300 international journals (including Progress in Polymer Science, Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, and Advanced Functional Materials, etc), project proposals from American Chemical Society, Hong Kong Research Grants Council, etc, and book proposals from Springer, Elsevier and CRC. He has published two books (Thin film shape memory alloys – fundamentals and device applications, Polyurethane shape memory polymers) and is currently on the editorial board of over three dozen of journals.
Summary :
A new and upgraded approach to the diseased states and wellness resulted in a new trend in the healthcare services, namely, personalized and precision medicine (PPM). The latter does need to be drastically and globally re-armed and re-innovated! To achieve the implementation of PPM con-cept, it is necessary to create a fundamentally new strategy based upon the biomarker-guided target-ing and bionavigating to have a unique impact for the implementation of PPM model into the daily Clinical Practice, Biotech and Biopharma. In this sense, despite breakthroughs in research that have led to an increased understanding of PPM-controlled human disease, the translation of discoveries into therapies for patients has not kept pace with medical need. It would be extremely useful to in-tegrate data harvesting from different databanks for applications such as prediction and personali-zation of further treatment to thus provide more tailored measures for the patients and persons-at-risk resulting in improved outcomes and more cost effective use of the latest health care resources including diagnostic (companion ones and/or theranostics), preventive and therapeutic (targeted molecular and cellular) etc. Bio-designers, Bioengineers and Biomanufacturers are beginning to realize the promise of PPM, translating to direct benefit to patients or persons-at-risk. For instance, companion diagnostics tools (CDTs), theranostics and targeted therapies represent important stakes for the Biotech & Biopharma, in terms of market access, of return on investment and of image among the prescribers.
About Author :
A new and upgraded approach to the diseased states and wellness resulted in a new trend in the healthSergey Suchkov was born in the City of Astrakhan, Russia, in a family of dynasty medical doc-tors. In 1980, graduated from Astrakhan State Medical University and was awarded with MD. In 1985, Suchkov maintained his PhD as a PhD student of the I.M. Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy and Institute of Medical Enzymology. In 2001, Suchkov maintained his Doctor De-gree at the National Institute of Immunology, Russia. From 1989 through 1995, Dr Suchkov was being a Head of the Lab of Clinical Immunology, Helmholtz Eye Research Institute in Moscow. From 1995 through 2004 - a Chair of the Dept for Clinical Immunology, Moscow Clinical Re-search Institute (MONIKI). In 1993-1996, Dr Suchkov was a Secretary-in-Chief of the Editorial Board, Biomedical Science, an international journal published jointly by the USSR Academy of Sciences and the Royal Society of Chemistry, UK.care services, namely, personalized and precision medicine (PPM). The latter does need to be drastically and globally re-armed and re-innovated! To achieve the implementation of PPM con-cept, it is necessary to create a fundamentally new strategy based upon the biomarker-guided target-ing and bionavigating to have a unique impact for the implementation of PPM model into the daily Clinical Practice, Biotech and Biopharma. In this sense, despite breakthroughs in research that have led to an increased understanding of PPM-controlled human disease, the translation of discoveries into therapies for patients has not kept pace with medical need. It would be extremely useful to in-tegrate data harvesting from different databanks for applications such as prediction and personali-zation of further treatment to thus provide more tailored measures for the patients and persons-at-risk resulting in improved outcomes and more cost effective use of the latest health care resources including diagnostic (companion ones and/or theranostics), preventive and therapeutic (targeted molecular and cellular) etc. Bio-designers, Bioengineers and Biomanufacturers are beginning to realize the promise of PPM, translating to direct benefit to patients or persons-at-risk. For instance, companion diagnostics tools (CDTs), theranostics and targeted therapies represent important stakes for the Biotech & Biopharma, in terms of market access, of return on investment and of image among the prescribers.
Summary :
To enhance the lifetime of mechanical system such as automobile, new reliability methodology – parametric Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) – suggests to produce the reliability quantitative (RQ) specifications— mission cycle—for identifying the design defects and modifying them. It incorporates: (1) a parametric ALT plan formed on system BX lifetime that will be X percent of the cumulated failure, (2) a load examination for ALT, (3) a customized parametric ALTs with the design alternatives, and (4) an assessment if the system design(s) fulfil the objective BX lifetime. So we suggest a BX life concept, life-stress (LS) model with a new effort idea, accelerated factor, and sample size equation. This new parametric ALT should help an engineer to discover the missing design parameters of the mechanical system influencing reliability in the design process. As the improper designs are experimentally identified, the mechanical system can recognize the reliability as computed by the growth in lifetime, LB, and the decrease in failure rate. Consequently, companies can escape recalls due to the product failures from the marketplace. As an experiment instance, two cases were investigated: 1) problematic reciprocating compressors in the French-door refrigerators returned from the marketplace and 2) the redesign of hinge kit system (HKS) in a domestic refrigerator. After a customized parametric ALT, the mechanical systems such as compressor and HKS with design alternatives were anticipated to fulfil the lifetime – B1 life 10 year.
About Author :
Dr Woo has a BS and MS in Mechanical Engineering, and he has obtained PhD in Mechanical Engineering from Texas A&M. He majors in energy system such as HVAC and its heat transfer, optimal design and control of refrigerator, reliability design of thermal components, and failure Analysis of thermal components in marketplace using the Non-destructive such as SEM & XRAY. In 1992.03–1997 he worked in Agency for Defense Development, Chinhae, South Korea, where he has researcher in charge of Development of Naval weapon System. He was working as a Senior Reliability Engineer in Refrigerator Division, Digital Appliance, SAMSUNG Electronics. Now he is working as associate professor in mechanical department, Ethiopian Technical University.
Summary :
In this research work, the energy band gap of Bi & Li doped BaTiO3 has been reduced by the incorporation of metal ion (Fe+3). The results show that the lattice distortion as well as the defect formation in the perovskite unit cell gives rise to a narrower band gap which is useful for photovoltaic applications. Solid state reaction method was followed to prepare the samples. Five samples were prepared with different Fe concentrations Ba0.96Bi0.02Li0.02Ti1-xFexO3, where x = 0.00, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08. The powders were weighed and ground using ball milling for 4 hours. The powders were kept for calcination at 1100 ˚C for 6 hours. Afterwards, the calcined powders were axially pressed to form circular pellets which kept for sintering at 1250 ˚C for 4 hours using conventional furnace. The structural investigations were confirmed via XRD and Raman analyses. Measurements showed crystal structure transition from tetragonal to hexagonal phase with respect to the Fe concentration. Rietveld refinement was performed to obtain the structural information. The octahedral distortion and the average bond length variation have been calculated to interpret the variation in the energy band gap. This material has shown the Jahn-Teller effect which gives rise to 3d orbital splitting leading to narrower band gap. The optical band gaps were calculated using Tauc-plot and Kubelka-Munk function from the DRS spectra. To confirm the existence of oxygen vacancies, ESR measurement has been carried out and analyzed. The energy band gap of the sample x = 0.08 showed the narrowest band gap of 2 eV, which paves the way for this composition to be used for visible range photovoltaic applications.
About Author :
My name is Othman Ali, Iraqi national. I have completed my BSc. from School of Physics, Tikrit University, Iraq. Afterwards, I studied MSc. in Physics, Department of Studies in Physics, Mysore University, India. Now I am pursuing my Ph.D. in Physics, School of Physics, University of Hyderabad, India.
Summary :
Lithium-ion batteries (LIB) have become one of the main storage devices for consumer electronic products. Natural vein graphite has been identified as a potential anode material in LIB, with a purity requirement of over 99.5%. The HCl acid leaching purification method has shown its success in achieving that target at laboratory scale. However, in order to move to commercial production, the purification process needs to be scaled up. Already, a considerable gap exists between laboratory-level achievements and commercialization. In this perspective, making prior scientific predictions of the purity of scaled-up purified graphite will make it easier to make more accurate scientific decisions on the scaling-up process. For that, purified graphite samples were scaled up using the quartile formula at the laboratory level, and the developed graphite samples were characterized. A linear regression model was then developed to predict the purity of the scaled-up graphite with the higher volumes of acid-leached solution used in the HCl acid leaching method. The resulting model showed a significant P-value of 0.000, indicating that it is feasible and effective in forecasting the purity of the scaled-up graphite samples. The fitted model could explain 99.54% of the variation in the volume of acid solution used in the HCl acid leaching method. The model was validated, and its assumptions were verified by performing residual analysis with a significance level. The present study reveals that the best linear regression model for higher volumes was developed using proportional rules for masses and volumes in accordance with the quartile formula. Therefore, this approach could be beneficial in generating precise scientific predictions to scale up the purification process of vein graphite.
About Author :
Himashee Naranpanawa is a postgraduate researcher attached to the National Center for Advanced Battery Research (NCABR) of National Institute of Fundamental Studies, Kandy, Sri Lanka. She received her B.Sc. in Mineral Resources and Technology specializing Mineral Processing Technology from the Uva Wellassa University of Sri Lanka in 2017 and currently reading for the M.Phil. Degree from the University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. Her research work focuses mainly on purification/modification aspects of natural vein graphite with special attention on scaling-up/optimization, for the anode application in rechargeable batteries.