Diabetes
Summary :
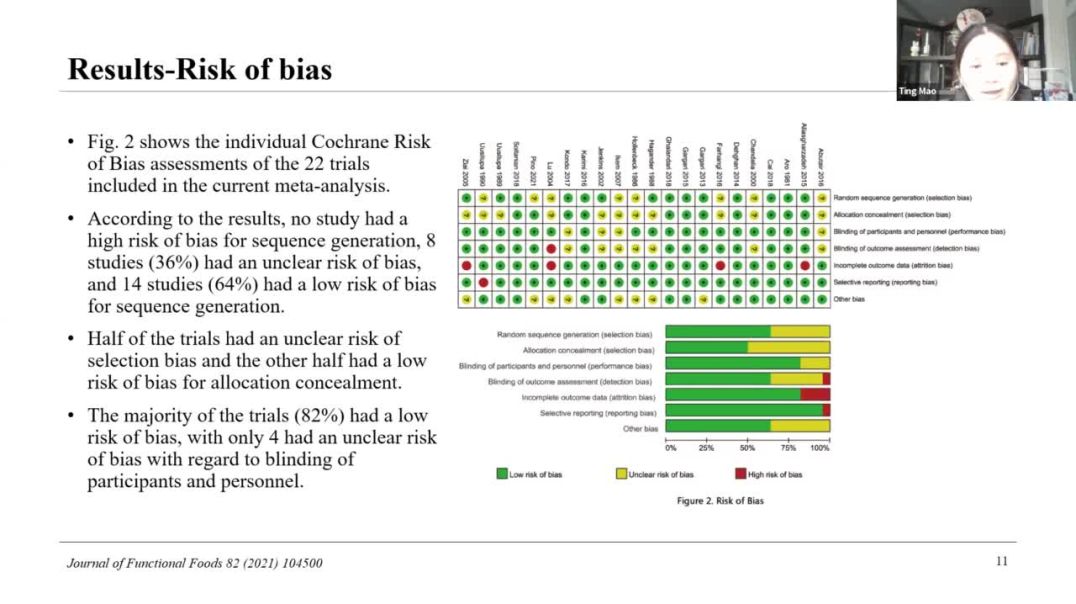
This review aimed to assess the effect of dietary fiber on short-term and long-term glycemic control and insulin responses in T2DM patients. Five electronic databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in English and investigating one primary outcome—glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and six secondary outcomes—fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin, Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), two-hour postprandial glucose, two-hour postprandial insulin, and body mass index (BMI) through March 23, 2021. Of 3266 identified studies, 22 eligible RCTs comprising 911 participants with T2MD were included. Among them, 16 studies used soluble fiber and the rest used fiber from natural foods. Subgroup analysis demonstrated that soluble fiber was more efficient in controlling HbA1c and FBG than fiber from natural foods. Compared with the control, dietary fiber at a median dose of 10 g/day for a median intervention duration of 8 weeks significantly reduced HbA1c, FBG, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR. In conclusion, both soluble fiber products and fiber from natural foods are effective in improving glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in T2MD patients, the former yielding better effects. However, due to most of the evidence from rather short-term trials and the detected significant between-study heterogeneity, further long-term and high-quality RCTs are needed.
About Author :
I am a register dietitian and psychological consultant in China. I got my master’s degree in Nutrition and Dietetics in Saint Louis University and after that, I came back to China to work as a dietitian for around 7 years and now I am pursuing my PhD in Food Science in Lincoln University. My research is mainly focus on exploring the health effects of bioactive ingredients such as dietary fiber and polyphenols. I am also interested in discovering milk proteins as delivery vehicles for beneficial compounds.
Summary :
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) report, 35,000 diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) in 2017 (1). Improving glycemic control decreases the risk of diabetic complications. Annual cost of treating diabetic patients with complications was US$11,706.9 compared with US$2746.7 for treating those without complications (2). Using FGM gives more insight for the physician and patient to manage diabetes, and thus, improve glycemic control.
About Author :
Bachelor’s degree in pharmaceutical science, king Saud university 2012 Master’s in health informatics, king Saud university 2020 Senior pharmacist at Prince Sultan Cardiac center.
Summary :
As of today, approximately over 400 million adults are diagnosed with Diabetes, and another 300 million adults have been found to have shown impaired glucose tolerance, and render at a high risk for developing the disease. The clinical condition wherein men show the symptoms and biochemical evidences of deficient testosterone levels is known as male hypogonadism, and it, with stern evidences, has been to be prevalent, with a greater tendency, in men with type 2 diabetes. Low testosterone is associated with diminished libido, erectile dysfunction, increased fat mass, decrease muscle, bone mass and energy, depression and anaemia.Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism related with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus has been an ever growing concern, and we shall be discussing the implications and co-effects of this, in this session.
About Author :
Shikhar Tripathi is a medical student, researcher and an author. Even as a student, he has published multiple research as well as review articles, which have received global acclaim, and has authored two medical reference books. One of his articles, where he gave a hypothesis on vertical transmission of COVID-19 from pregnant mother to fetus, was well acclaimed world wide and even got featured by Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in their repository and also got featured amongst the references on COVID-19 researches, on Wikipedia. He has been a guest speaker for the Young Researcher’s Forum at International Conference on Diabetes, Hypertension and Metabolic Syndrome 2020, International Conference on COPD and Asthma 2021 and is slated to be a guest speaker at International Conference on Clinical & Pharmaceutical Microbiology, 2021 (to be held in November 2021).
Summary :
This cross-sectional, web-based study included Saudi adult patients with T1DM who attended at least one virtual phone visit with the diabetes clinic at King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, between August 1 and December 31, 2020. Patients anonymously answered a Google form- created Arabic questionnaire. Information about patient characteristics, outcome, and perception of the virtual phone visit were obtained. Data were presented using descriptive statistics, chi-square, one- way ANOVA, independent t-, and Welch’s t-tests.
Summary :
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is an endocrine disease characterized by hyperglycemia. According to WHO, 422 million people worldwide have diabetes and it is one of the leading causes of death in the world. α-Glucosidase and α-amylase can hydrolyze carbohydrates; thus, inhibitors of these enzymes are considered useful drug candidates for type II DM therapy. Long-term use of synthetic enzyme inhibitors, such as acarbose, may cause various side effects, such as flatulence and abdominal problems. Natural α-glucosidase inhibitors have thus been presented as a better alternative to control postprandial hyperglycemia as they exhibit minor or no side effects. The aim of this study is the scientific investigation of antihyperglycemic effect of 70% methanol extracts prepared from 32 plants used traditionally against diabetes in Turkey. The plants were collected from Erzurum and its environs in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Then, they were dried, powdered, and extracted. The extracts were evaluated for in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. The inhibitory activity was determined spectrophotometrically by measuring the quantity of p-nitrophenol released from p-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside at 405 nm. Cotinus coggygria (leaves), Rhus coriaria (fruits), Viburnum opulus (fruits), Viburnum lanata (fruits), Paeonia mascula (aerial parts), Elaeagnus angustifolia (leaves), Elaeagnus rhamnoides (leaves), Paliurus spina-christi (fruits), Pinus sylvestris (cones), Juniperus foetidissima (cones), Juniperus oxycedrus (cones), and Prunus spinosa (fruits) showed the potent inhibitory activity with >90% inhibition at 5 mg/mL when compared with acarbose as a standard drug with 67% inhibition at same concentration. In addition, the compounds responsible for α-glucosidase inhibitory activity were isolated from some of these plants.
About Author :
She graduated from Atatürk University, Faculty of Pharmacy in 2013. She graduated and get PhD from Atatürk University Health Sciences Institute in 2020. She has been working as a Research Assistant at Atatürk University, Faculty of Pharmacy since 2014. While continuing her doctoral education; within the scope of Erasmus+ Program, she conducted studies in her field under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Karel Smejkal (VFU, Brno/Czechia) in 2017; Prof. Dr. Rudolf Bauer (Graz University, Graz/Austria) in 2020. She also works as a researcher and educator at Atatürk University Medicinal and Aromatic Plant and Drug Research Center. Her research areas are as follows: Phytochemistry, Biological activities (in vitro alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase activities, antioxidant activities), Analytical pharmacognosy.
Summary :
Diabetes is a multifactorial disease with complex multi-organ-multi-target crosstalk in the body. While the currently available molecular drugs effectively reduce hyperglycemia, they are inadequate to address the multifactorial etiopathology, chronicity and systemic complications of diabetes. A more holistic and systemic approach is essential for the successful management diabetes and associated metabolic diseases. We hypothesize an integrative diabetes management strategy, combining holistic principles of diabetes management with its molecular understandings, would be more appropriate to fill this gap. We propose a novel trans-disciplinary ‘Ayurveda-Biology’ approach for deepening the holistic understanding of the pathophysiology of diabetes as well as designing novel integrative strategies for managing diabetes and restoring whole body glucose homeostasis. While Ayurveda and modern biomedicine uses different epistemology and ontology for describing diabetes, both the systems recognize the central role of gut and gut derived factors in postprandial glucose disposal and whole body glucose homeostasis. Essentially, the principles of both Ayurveda and modern biomedicine overlap at a gut centered view of diabetes management; and Gastro-intestinal mediated glucose disposal, a holistic concept of glucose metabolism. Therefore, an integrative disease management strategy, focusing on an Ayurveda Biology framework, would be the prerogative for successful management of diabetes. This can also offer novel strategies for cost effective, holistic and multi-targeted management of diabetes.
About Author :
A researcher, trained in cell biology and molecular biology, with more than 10 years of research and teaching experience at various institutes and Universities in India and South Korea. Interested in medical pluralism and integrative medicine for wellness and disease management. My research interests are metabolic diseases, with special focus on glucose metabolism and its role in obesity and diabetes. Our team is working on creating trans-disciplinary knowledge framework between Ayurveda, the traditional Indian System of Medicine (ISM) and modern biology for delineating the complex biology of metabolic homeostasis and metabolic diseases. Our team envisage that the effective merger of both holistic and reductionist views of biology is imperative for successful health and disease management. Recognizing and logically bridging epistemologically and culturally different perspectives of health and disease management would have significant contribution in the contemporary healthcare sector, particularly in the management of chronic lifestyle diseases.
Summary :
M. pumilum has been claimed to protect the bone against the adverse effect of estrogen deficiency. Additionally, it also exhibits anti-diabetic activity. In view of these, this study aims to identify the mechanisms underlying the bone protective effect of M. pumilum in the presence of both estrogen deficiency and diabetes mellitus (DM). Methods: Ovariectomized, diabetic female rats were given M. pumilum leave aqueous extract (MPLA) (50 and 100 mg/kg/day), estrogen, glibenclamide and estrogen plus glibenclamide for 28 consecutive days. At the end of the treatment, fasting blood glucose (FBG), serum insulin, Ca2+, PO4 3- and bone alkaline phosphatase (BALP) levels were measured. Rats were sacrificed and femur bones were harvested for determination of expression level and distribution of RANK, RANKL, OPG and oxidative stress and inflammatory proteins by molecular biological techniques.
About Author :
Dr. Giribabu Nelli, Senior Lecturer in the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya. In 2011 November, Dr. Giribabu Nelli completed his Ph.D. in reproductive and developmental biology at the Department of Zoology, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, India. From 2013 to 2016, he worked as a postdoctoral fellow at the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, the University of Malaya. In the same Department, he was recruited as a Senior Lecturer in November 2016. He has now published 61 ISI publications with a high impact factor, as well as two book chapters and two patents (Filed) with achieved 6 grants. His main research interests on diabetes and their complications, obesity, natural products and male and female reproductive physiology.
Summary :
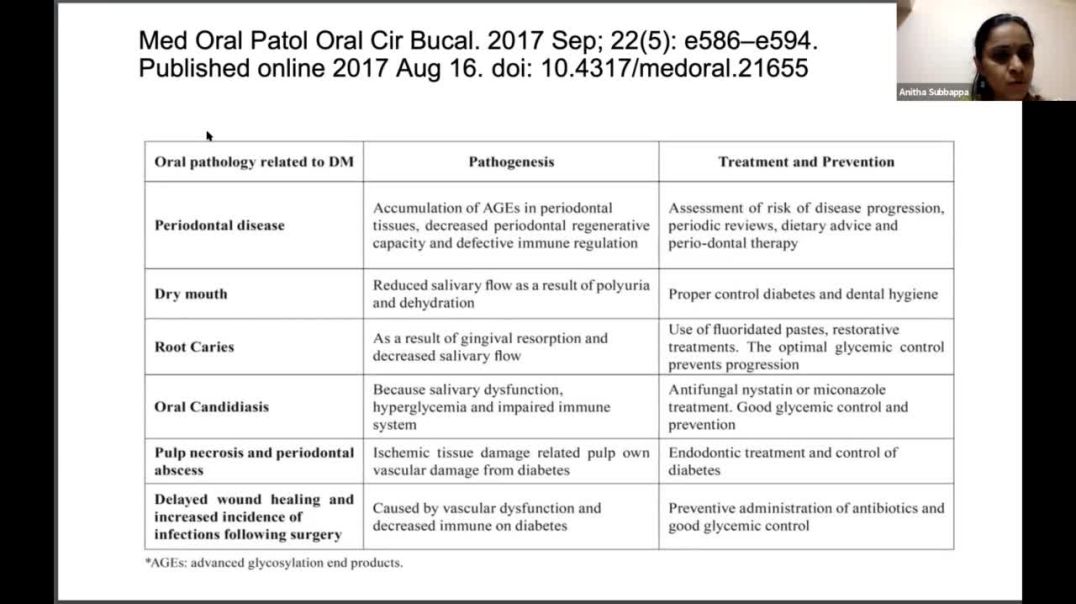
Diabetes mellitus, a major lifestyle disease, has become a global burden. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF), Diabetes Atlas (2015), reports that there are 415 million people diagnosed with diabetes representing 8.8% of adults aged 20–79 years. A knowledge on oral lesions to help diagnose a case of diabetes which would also require a referral to endocrinologist. Also a 2 way link has been established between diabetes & periodontitis. A physician/endocrionologist/diabetologist needs to be aware of oral changes to be able to form an interdisplinary unit for a comprehensive handling of patients. An awareness of periodontitis as the 6th Complication of Diabetes is also important. Dental caries/periodontitis, black hairy tongue, candidiasis, Xerostomia & other mucosal lesions are also a frequent finding in diabetic patients. A knowledge on the oral changes and its entity in diabetic complications stresses the importance of dental element in diabetes.
About Author :
She is a Reader in the Department of periodontology, JSSDCH, JSSAHER with 20 years experience. She has authored national and international publications. She has presented papers nationally and internationally, won nationally and international awards. She is a Laser Specialist from SOLA, University of Vienna. She is an implantolgist. She has been a Speaker in National Conferences. She is the Team Leader of Special Interest Group “Diabetes & Oral Care.” She is a member of Geriatric clinic at JSS Multi Speciality Hospital. She is a reviewer in various journals. She has been a chairperson, judge/panelist at conferences. She has organized various webinars/conferences/epaper/eposter competitions. he is a member at various Dental societies. She has authored a book. She has guided Undergraduates/postgraduate research/paper presentations, winning awards.