Materials Space-Tectonics | Yusuke Yamauchi
Summary :
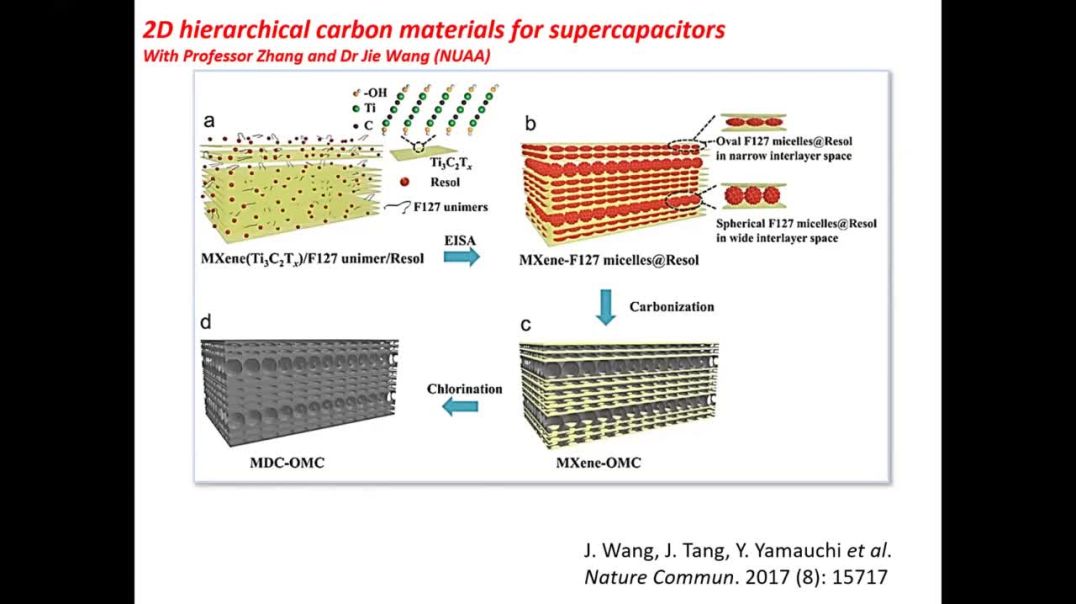
Different types of inorganic nanomaterials have been designed by using various methods including sol-gel, electrochemical/chemical reduction, calcination, hydrothermal reaction, etc. The dimensionality of these nanomaterials (x, y, z) can be classified as zero-dimensional (0D), one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D), or three-dimensional (3D), respectively. Accordingly, for 0D nanomaterials dimensions are measured on the nanoscale (< 100 nm for each dimension). 0D nanomaterials, for example nanoparticles (or sometimes, nanocrystals), most commonly have isotropic morphologies where the usually thermodynamically stable planes of lower reactivity are exposed at the nanoparticles’ surfaces. For 1D nanomaterials, a single dimension is extended beyond the nanoscale. This class of nanomaterials includes nanotubes, nanorods, and nanowires. In contrast to 0D and 1D nanomaterials, 2D nanomaterials have recently attracted great interest for the next generation of promising. However, such 2D materials are often formed by stacking/assembly, processes that vastly reduce their active surface areas, and negatively affects their performance in potential applications.