The effect of rippling on the mechanical properties of graphene | Guillermo
Summary :
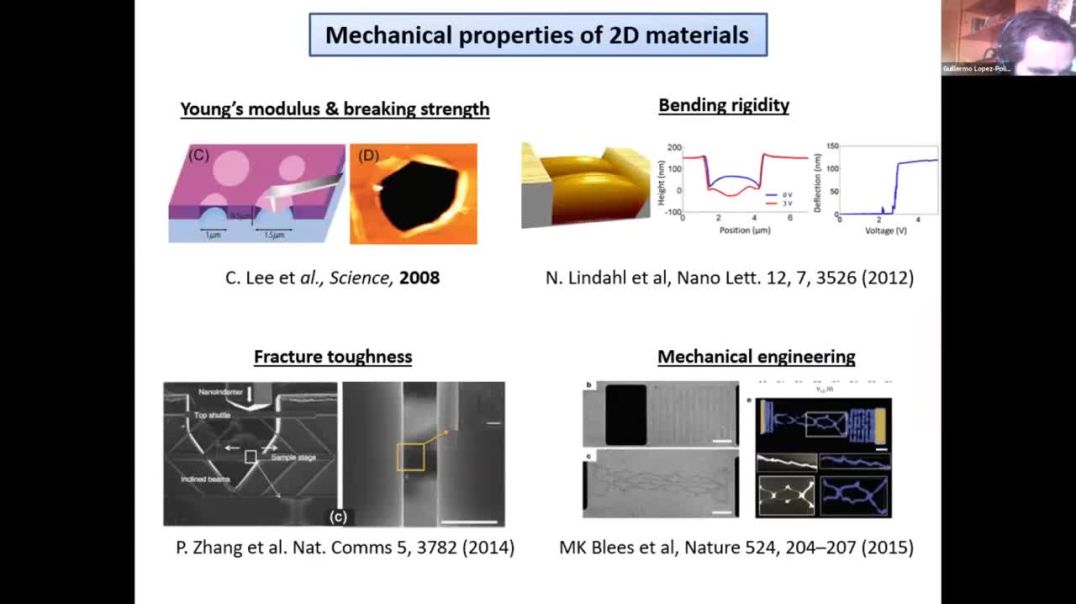
Graphene is the paradigm of membranes; it is the stiffest material known so far and it is extremely bendable due to its one atom thickness. As a consequence free-standing graphene exhibit ripples that has major effects on its elastic properties. I will briefly summarize three experiments performed in our group where the influence of rippling is essential to address the results. Firstly, we observed that atomic vacancies lessen the negative thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) of free-standing graphene. We also observed an increase of the Young’s modulus with global applied strain and with the introduction of small density defects that we attributed to the decrease of rippling. The results can be qualitatively explained in the framework of the elastic theory of membranes that predicts a reduction of the Young’s modulus, an increase of the bending rigidity and a decrease of the area with the rippling. However, our results diverge quantitatively from the theoretical predictions: the experiments consistently indicate that only the rippling with wavelengths between 5 and 10 nm influences the mechanics of graphene. The rippling responsible of the negative TEC and anomalous elasticity is thought to be dynamic, i.e. flexural phonons. However, flexural phonons with these wavelengths should have minor effects on the mechanics of graphene, therefore other mechanisms must be considered to address our observations. We propose static ripples as one of the key elements to correctly understand the thermomechanics of graphene and suggest that rippling arises naturally due to a competition of symmetry breaking and anharmonic fluctuations.