Challenges in the development of lead free piezoelectrics for electromechanical applications | Paula
Summary :
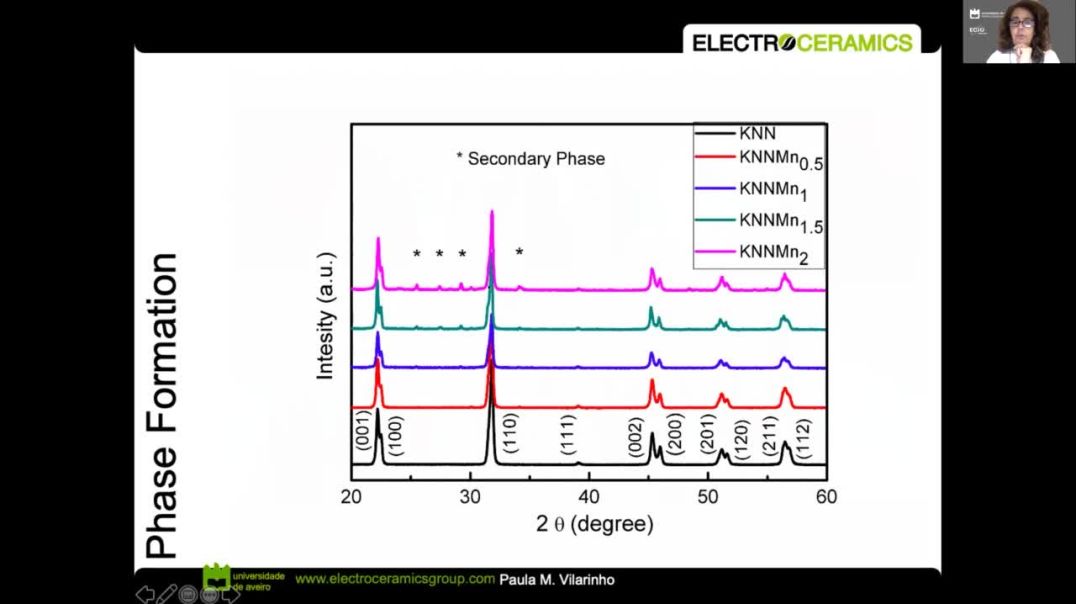
The global piezoelectric devices market is estimated to grow from USD 28.9 billion in 2020 to USD 34.7 billion by 2025; at a CAGR of 3.7%. Key factors driving the growth of this market include the rising demand for piezoelectric devices for energy harvesting, aerospace & defense applications [1]. The market has been dominated by the solid solution of lead zirconate titanate, namely PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 (PZT), that exhibits unique piezoelectric properties with maximized figures of merit. However, environment issues and health concerns associated with Pb toxicity are currently driving the search for alternative lead free piezoelectrics. In this talk the opportunities and challenges in the development of lead free piezoelectrics for electromechanical applications are presented and discussed. The leading PbO-free candidates replacements are (K1-xNax)NbO3.(KNN), (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 (BNT) and (Ba,Ca)(Zr,Ti)O3 (BCZT). KNN remains the most promising lead-free piezoelectric system to replace PZT. The electromechanical properties are still inferior to PZT but its high Curie temperature (TC = 420°C) potentially facilitates higher temperature applications and limits issues of de-poling, which are significant problems for BNT and BCZT. In addition, the control of sintering and general ceramic engineering of KNN is far from complete, prompting opportunities for improvements in processing. In this talk I will describe the interplay between materials structure, microstructure, electrical conductivity, and non-linear dielectric properties for KNN ceramics and single crystal prepared by a set conventional and non-conventional sintering processes and the implications of these relations for enhancing the electromechanical performance [2-7].
About Author :
Prof Paula Vilarinho is the professor at Department of Materials and Ceramic Engineering (DEMaC), Centre for Research in Ceramics and Composites, CICECO, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal.